How to operate a drone unveils the fascinating world of unmanned aerial vehicles. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, from understanding the various components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll cover everything from basic controls and safety procedures to legal considerations and maintenance, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
We’ll explore the intricacies of different drone types, their functionalities, and the importance of adhering to safety regulations. This detailed guide will empower you to navigate the airspace safely and effectively, capturing breathtaking aerial footage along the way. Whether you’re a novice or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this guide will serve as your ultimate resource for becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Drone Parts and Components: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of key parts and explores the differences between various drone types.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated work of several key components. Let’s examine each one:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller is a miniature computer that processes sensor data and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates inputs from various sensors such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers.
- Battery: The power source for the entire system, the battery’s capacity determines flight time. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are widely used due to their high energy density.
- GPS: The Global Positioning System provides location data, enabling autonomous flight features like waypoint navigation and return-to-home functionality. Accuracy varies depending on GPS signal strength and environmental factors.
- Camera: Many drones incorporate cameras for capturing aerial photos and videos. Camera quality varies significantly between models, affecting image resolution, field of view, and video capabilities.
Drone Type Variations
Drones come in various configurations, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types are:
- Quadcopter: Four rotors provide stability and maneuverability. This is the most common type of consumer drone.
- Hexacopter: Six rotors offer increased redundancy and stability, making them suitable for heavier payloads or more challenging flying conditions.
- Octocopter: Eight rotors provide exceptional stability and payload capacity, often used for professional applications like aerial cinematography or surveying.
The number of rotors affects the drone’s stability, payload capacity, and flight time. More rotors generally mean greater redundancy and stability but may also increase weight and complexity.
Popular Drone Model Comparison
The following table compares the specifications and features of three popular drone models (Note: Specifications are illustrative and may vary depending on the specific model and version):
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Flight Time | 30 minutes | 25 minutes | 40 minutes |
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| GPS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Weight | 1.2 kg | 0.8 kg | 1.5 kg |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for responsible drone operation. This section Artikels these crucial steps.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow this checklist to ensure safe operation:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check the controller’s battery level.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm airspace regulations and restrictions for your flight location.
- Inform others of your flight plans, if necessary.
Safety Guidelines and Legal Regulations
Drone operation is subject to various regulations and guidelines to ensure safety and prevent accidents. These vary by location, so always check local laws before flying. Some common safety guidelines include:
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near airports, airfields, or other restricted airspace.
- Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Never fly your drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be aware of surrounding obstacles and avoid collisions.
- Fly responsibly and ethically.
Emergency Procedures
Unexpected situations can occur during drone operation. Being prepared for emergencies is crucial. Here are some procedures to follow:
- Low Battery: Initiate the return-to-home function immediately if the battery level becomes critically low.
- Unexpected Malfunctions: If the drone malfunctions, attempt to regain control. If unsuccessful, prioritize safety and allow the drone to land safely (if possible).
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a return-to-home feature that activates when the signal is lost. However, it’s essential to maintain a close visual on the drone’s trajectory.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers

Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section covers fundamental maneuvers.
Basic Flight Controls
Most drones use a controller with four primary controls:
- Throttle: Controls altitude; pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases it.
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement; tilting the stick forward moves the drone forward, tilting it backward moves it backward.
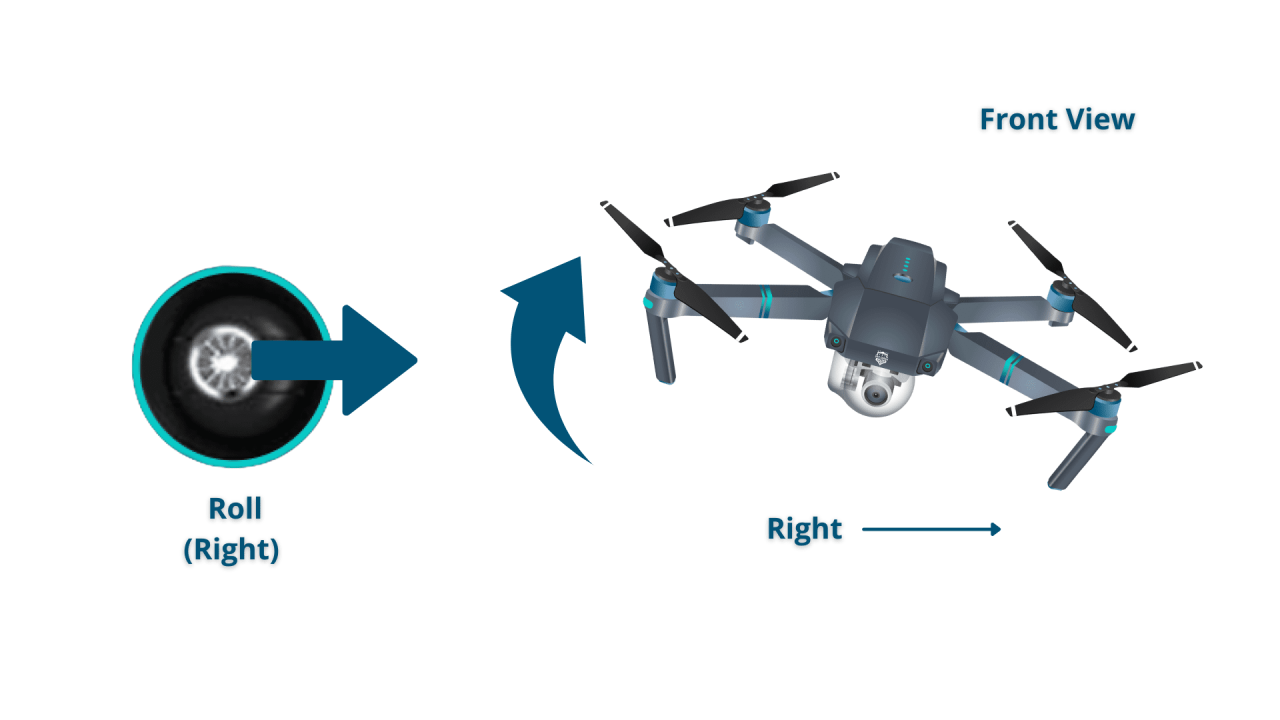
- Roll: Controls left and right movement; tilting the stick to the left moves the drone left, tilting it to the right moves it right.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis; rotating the stick left or right rotates the drone left or right.
Basic Maneuvers
Practice these basic maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights:
- Taking Off: Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Landing: Gradually decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady altitude and position by precisely controlling the throttle.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use a combination of pitch, roll, and yaw controls to move the drone in the desired direction.
Figure-Eight Flight Pattern
Performing a figure-eight pattern demonstrates control and coordination. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Hover at a comfortable altitude.
- Move forward in a straight line for a short distance.
- Begin a smooth turn to the right, creating the top half of the figure eight.
- Continue the turn, moving backward and then to the left, completing the bottom half of the figure eight.
- Return to the starting position.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, you can explore more advanced techniques for smoother and more precise flight.
Advanced Flight Techniques
These techniques require practice and skill:
- Precise Hovering: Maintaining a steady position without drifting requires precise control of the throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw.
- Smooth Transitions: Moving between different maneuvers without abrupt changes in speed or direction requires coordination and practice.
- Waypoint Navigation: Using pre-programmed points to guide the drone’s flight path offers greater control and precision.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability:
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS data for position holding and autonomous flight features.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its starting position, regardless of GPS signal.
- Manual Mode: Provides direct control over the drone’s motors, offering maximum maneuverability but requiring more skill.
Weather Conditions and Mitigation Strategies
Weather significantly impacts drone flight. Wind, rain, and extreme temperatures can affect stability and performance. Always check the forecast before flying and avoid flying in adverse conditions.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Camera Settings
Camera settings significantly influence image quality. These include:
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens, affecting depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light, affecting motion blur.
- ISO: Measures the sensor’s sensitivity to light, affecting image noise.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
To capture high-quality aerial media:
- Use a high-quality drone with a good camera.
- Optimize camera settings for the lighting conditions.
- Keep the drone stable to minimize motion blur.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Aerial photography and videography offer unique compositional possibilities. Consider these aspects:
- Leading Lines: Use roads, rivers, or other features to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements off-center for a more visually appealing composition.
- Perspective: Experiment with different altitudes and angles to capture unique perspectives.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Follow this schedule for optimal drone performance:
- Inspect propellers for damage after each flight.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens regularly.
- Check and tighten all screws and connections periodically.
- Store the drone and battery in a cool, dry place.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors regularly.
- Update the drone’s firmware as needed.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Motor Failures: Inspect the motor for damage and replace if necessary.
- Battery Problems: Ensure the battery is properly charged and in good condition. Replace if necessary.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure a clear view of the sky and try restarting the drone.
- Gimbal Issues: Recalibrate the gimbal or check for physical obstructions.
Troubleshooting Guide
A systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential. Start with the simplest solutions and progressively investigate more complex issues.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation requires understanding and adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines.
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions

Drone laws vary by location. Always check local regulations before flying. Common restrictions include no-fly zones near airports and other sensitive areas.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount. Respect privacy, obtain permission before flying over private property, and avoid reckless or dangerous flying.
Best Practices
Responsible drone operation involves respecting laws, privacy, and safety. Always fly safely and ethically.
Drone Software and Apps
Drone software and apps provide control, configuration, and data management capabilities.
Drone Software and App Functionalities
These applications provide essential functions for operating and managing your drone.
Comparing Drone Control Apps, How to operate a drone
Various apps offer different features and usability. Consider factors like ease of use, advanced features, and compatibility when choosing an app.
Popular Drone App Comparison
The following table compares three popular drone apps (Note: Features may vary depending on the app version and drone model):
| Feature | App A | App B | App C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flight Control | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Camera Control | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Waypoint Navigation | Yes | No | Yes |
| Live Video Feed | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technology, skill, and responsibility. This guide has provided a foundation for safe and effective drone piloting, emphasizing the importance of understanding your equipment, adhering to regulations, and prioritizing safety. By mastering the techniques Artikeld, you can confidently explore the exciting possibilities of aerial photography and videography while respecting the airspace and those around you.
Remember that continued practice and a commitment to responsible flying are key to becoming a skilled and ethical drone operator.
FAQ Corner
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes for many consumer drones, but larger models can fly much longer.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide will help you confidently navigate the complexities of drone operation and ensure a smooth and successful flight experience every time.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations in your area.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, carefully bring the drone back manually, keeping it within visual range.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure you operate your drone responsibly and safely.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or if the drone has experienced a significant impact.